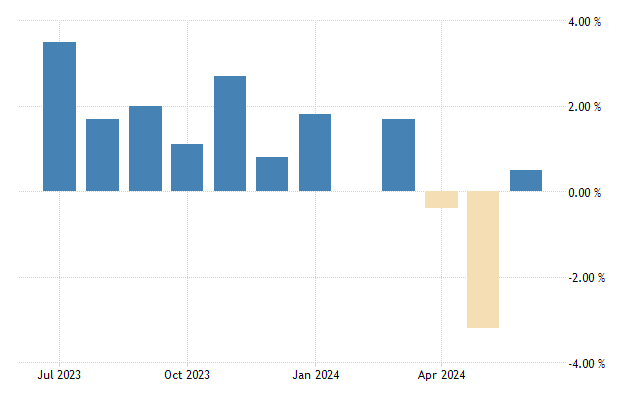Trading Economics Inflation
Extension is an essential monetary thought that impacts each piece of an economy, from the expenses of work and items to wander decisions and cash-related procedures. With the rising multifaceted design of overall business areas, understanding extension is more essential than some other time in ongoing memory. Trading Monetary issues, a phase known for its sweeping money-related data and examination offers significant encounters into development designs across various countries. This article jumps into the possibility of development, examines how Trading Monetary issues give significant data on extension, and checks out the implications of extension on different financial regions.
What is Expansion?
Expansion alludes to the rate at which the general degree of costs for labor and products rises, prompting a lessening in buying power. It is regularly estimated by the Customer Value Record (CPI) or Maker Value List (PPI). Expansion can be classified into a few kinds, including:
Request Pull Expansion: This happens when total interest surpasses total inventory, prompting greater costs.
Cost-Push Expansion: Results from an expansion in the expense of creation, for example, rising wages or unrefined substance costs, which pushes costs higher.
Underlying Expansion: Emerges from the versatile assumptions for expansion, where past expansion rates impact future cost increments.
The Job of Exchanging Financial matters and Figuring out Expansion
Exchanging Financial matters is the main stage that gives monetary information, conjectures, and verifiable patterns for different financial pointers, including expansion. The stage offers an easy-to-understand interface that empowers clients to get continuous information, envision drifts, and dissect expansion rates across various nations.
Elements of Exchanging Financial Aspects
Continuous Information: Exchanging Financial aspects gives exceptional expansion information from around the world. This incorporates month-to-month, quarterly, and yearly expansion rates, which assist clients with following changes in the cost for many everyday items and financial circumstances.
Authentic Information: The stage offers verifiable expansion information, permitting clients to investigate long-haul drifts and recognize designs over the long run.
Figures: Exchanging Financial aspects give expansion gauges in light of econometric models and well-qualified sentiments. These gauges assist clients with expecting future expansion patterns and pursuing informed choices.
Intelligent Diagrams: Clients can imagine expansion information through intuitive outlines, which make it more clear patterns, look at nations, and recognize huge monetary occasions.
Financial Schedule: The monetary schedule includes records of impending expansion reports and other key monetary pointers, assisting clients with remaining informed about significant information discharges.
How Exchanging Financial aspects Breaks down Expansion
Exchanging Financial Matters examines expansion through a mix of crude information, verifiable settings, and prescient models. This is the way the stage approaches expansion investigation:
Information Assortment: Exchanging Financial matters totals expansion information from true sources like public insights workplaces, national banks, and worldwide associations. This information is then normalized and introduced in a reliable configuration for simple correlation.
Verifiable Examination: The stage looks at authentic expansion patterns to give a setting to current information. This incorporates dissecting long-haul patterns, distinguishing verifiable inflationary periods, and figuring out the effect of past monetary arrangements.
Gauging Models: Exchanging Financial matters utilizes econometric models to create expansion estimates. These models think about different factors like financial development, money-related approaches, and outside shocks to anticipate future expansion rates.
Financial Markers: notwithstanding expansion information, Exchanging Financial matters consolidates other monetary pointers, for example, Gross domestic product development, joblessness rates, and loan fees, to give a far-reaching investigation of expansion and its consequences for the economy.
Ramifications of Expansion on the Economy
Expansion has broad ramifications for different monetary areas. This is the way expansion influences various parts of the economy:
Customer Spending
Expansion influences customer spending by diminishing buying power. As costs rise, purchasers might encounter a decrease in their genuine pay, prompting diminished spending on unnecessary labor and products. This can influence by and large monetary development and influence organizations that depend on customer spending.
Loan costs
National banks frequently change loan costs to oversee the expansion. At the point when expansion is high, national banks might increment loan costs to chill off the economy and forestall runaway expansion. Then again, during times of low expansion, national banks might bring down financing costs to animate monetary action. Changes in loan fees can impact acquiring costs, speculation choices, and purchaser conduct.
Venture
Expansion can influence venture choices by influencing the normal profits from speculations. High expansion might disintegrate the worth of fixed-pay ventures, like securities, while possibly helping the worth of resources like land and items that will generally perform well during inflationary periods. Financial backers might have to change their portfolios to relieve the impacts of expansion.
Wages and Business
Expansion can impact wage discussions and business conditions. During times of high expansion, laborers might request higher wages to stay aware of rising living expenses. This can prompt compensation expansion, which might additionally add to general expansion. Then again, low expansion might bring about more slow compensation development and decreased dealing power for laborers.
Government Strategy
Legislatures and national banks carry out financial and monetary arrangements to oversee the expansion. This incorporates changing loan costs, altering charge approaches, and executing spending programs. Viable arrangement measures are pivotal for keeping up with cost dependability and advancing reasonable financial development.
Contextual Investigations: Expansion Patterns Across Various Nations
In the US, expansion has been a huge financial concern, particularly during times of monetary flimsiness. The Central bank intently screens expansion and changes financial arrangements as needed. Late patterns have shown times of both high expansion, driven by inventory network disturbances and request vacillations, and low expansion, affected by financial log jams and strategy measures.
Eurozone
Expansion in the Eurozone has been impacted by a mix of elements, including variances in energy costs, financial development rates, and money-related strategies of the European National Bank (ECB). The ECB’s approaches expect to keep up with cost security across part nations, however, expansion patterns can differ altogether between nations inside the Eurozone.
Developing Business sectors
In developing business sectors, expansion rates can be more unpredictable because of elements like cash vacillations, political flimsiness, and monetary turn of events. Nations like Brazil, India, and Turkey have encountered critical inflationary tensions, which can influence monetary development and monetary security.
Expansion is an intricate and diverse monetary peculiarity that significantly affects different parts of the economy. Exchanging Financial matters gives important experiences into expansion through its far-reaching information, authentic investigation, conjectures, and intelligent devices. By understanding expansion patterns and their suggestions. People and organizations can settle on informed choices and explore the difficulties related to changing cost levels.
As the worldwide economy keeps on advancing, remaining informed about expansion and its belongings is pivotal. For compelling monetary preparation and navigation. Exchanging Financial matters offers an abundance of data that can assist clients with remaining in front of monetary patterns and pursuing vital decisions in a steadily changing financial scene.
Bits of knowledge from Exchanging Financial aspects
Expansion, the supported expansion in the general value level of labor and products after some time, is one of the most basic financial pointers for figuring out a country’s monetary well-being. It impacts financing costs, customer conduct, and government monetary arrangements. Exchanging Financial matters, a stage offering constant monetary information, gives itemized experiences into expansion patterns around the world, permitting financial backers, investigators, and policymakers to pursue informed choices. This article will dive into expansion from the perspective of Exchanging Financial aspects, investigating how the expansion is estimated, its circumstances and results, and the information-driven approach used to follow expansion drift internationally.
Grasping Expansion
Expansion alludes to the diminishing in the buying influence of cash, intending that as expansion rises, every unit of money purchases less labor and products. Expansion is regularly estimated utilizing two key files:
Customer Value Record (CPI): This action is the adjustment of the cost of a crate of buyer labor and products after some time. CPI is one of the most well-known signs of expansion and is utilized by national banks and states to check cost strength.
Maker Value List (PPI): This action is the typical change in selling costs by homegrown makers for their results. While CPI centers around buyers, PPI reflects changes in costs according to the viewpoint of makers.
Exchanging Financial matters offers continuous information on CPI and PPI for many nations, giving significant bits of knowledge into inflationary tensions.
Reasons for Expansion
Expansion can emerge from different variables, comprehensively classified into request-pull expansion and cost-push expansion:
Request Pull Expansion: This happens when total interest surpasses total stock. At the point when shoppers have more discretionary cash flow or organizations contribute intensely, interest in labor and products can surpass supply, driving up costs. National banks frequently endeavor to check request pull expansion by raising loan costs, which decreases getting and spending.
Cost-Push Expansion: This happens when the expense of creation builds, prompting more exorbitant costs for completed merchandise. Factors adding to cost-push expansion incorporate rising wages, expanded natural substance costs, and higher expenses or levies. Not at all like interest expansion, cost-push expansion can bring about slower financial development as organizations give greater expenses to buyers.
Financial Expansion: This happens when there is an excessive amount of cash coursing in the economy. This can happen when a national bank builds the cash supply without a comparing expansion in the development of labor and products, prompting a general expansion in costs.
Expansion Following: The Job of Exchanging Financial aspects
Exchanging Financial aspects tracks expansion information for north of 196 nations, giving point-by-point bits of knowledge into both month-to-month and yearly expansion rates. The stage offers admittance to:
Verifiable Information: Clients can see long-haul expansion patterns across various periods, empowering them to recognize examples, pinnacles, and times of steadiness.
Ongoing Expansion Information
Exchanging Financial matters gives cutting-edge expansion information when it is delivered by public measurable organizations, making it a significant asset for brokers, financial backers, and policymakers. The stage offers expansion gauges in light of current financial patterns, national bank strategies, and outer factors, for example, worldwide oil costs and production network disturbances. These estimates can assist organizations and financial backers with getting ready for possible inflationary shocks.
Examination Between Nations
Exchanging Financial matters permits clients to think about expansion rates across various nations and areas. This is especially valuable for organizations engaged with worldwide exchange, as expansion can influence money trade rates, import/send-out costs, and worldwide venture choices.
Impacts of Expansion on the Economy
Expansion has many consequences for both the economy and people. These impacts can be gainful or negative contingent upon the pace of expansion and the hidden financial circumstances.
Beneficial Outcomes of Expansion
Energizes Spending and Venture: Moderate expansion urges shoppers and organizations to spend or put away their cash instead of clutch it, as the buying force of money diminishes over the long run. This invigorates financial development, as more popularity can prompt more creation and occupation creation.
Diminishes the Genuine Worth of Obligation
Expansion decreases the genuine worth of obligation over the long haul, which can help borrowers. Assuming that wages expansion in accordance with expansion, obligation reimbursement becomes simpler, as borrowers reimburse their credits with cash that is worth less in genuine terms.
Supports Government Income: Expansion can assist states with expanding their income through higher assessment assortment. As wages and costs rise, so charge incomes, which can be utilized for public speculation and social projects.
Adverse consequences of Expansion
Dissolves Buying Power: One of the main drawbacks of expansion is its effect on buying power. As costs rise, shoppers can bear the cost of less labor and products with a similar measure of cash, decreasing their way of life, particularly in the event that wages don’t stay up with expansion.
Makes Vulnerability for Organizations: High expansion can prompt vulnerability in the business climate. Making it challenging at organizations to set costs, conjecture future expenses, and plan long haul ventures. This can prompt diminished business certainty and a lull in financial movement.
Financing cost Increments: National banks, like the Central bank in the US or the European National Bank. Frequently raise loan fees in light of rising expansion. Higher loan fees increment acquiring costs, which can decrease venture and utilization. Possibly prompting slow financial development or even a downturn.
From expansion in cutting edge economies to excessive inflation in developing business sectors, Exchanging. Financial matters assist clients with monitoring worldwide expansion patterns. Guaranteeing they stay on the ball in an undeniably unstable monetary scene. By utilizing information driven instruments and examination, organizations, financial backers, and policymakers can really answer inflationary tensions and diagram a course toward feasible monetary development.